KNN and SVM
Tags: Classification, KNN, Supervised, SVM, Week3
Categories: IBM Machine Learning
Updated:
K Nearest Neighbours
KNN is predicting the unknown value of the point based on the values nearby.
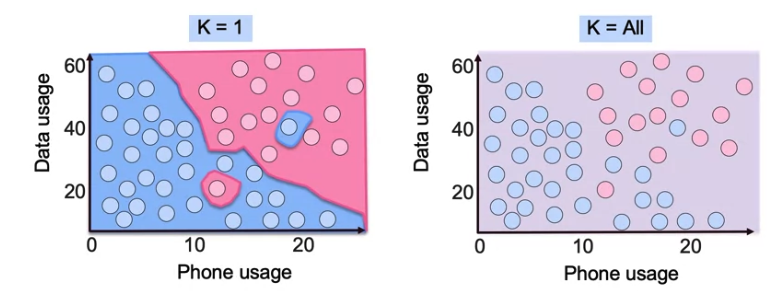
Decision Boundary
KNN does not provide a correct K such that the right value of K depends on which error metric is most importnat. Elbow method is a cmmon way to find the right value of K. We chose K from the kink of the error curve. It is choosing majority vote.
KNN Regression is prediction based on mean value of K neighbors. But slow computation because many distance calculation and does not generate insight innto data generating process.
Distant Measurement
- Euclidean distance L2
- Manhattan Distance L1
Scale for Distance Measurement
When the scale of X is small relative to the scale of Y, clustering the data may be inaccurate. Curse of dimensionality
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3) #by default, euclidean distance, also related to scale
knn = knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = knn.predict(X_test) #fit(x,y) and fit_transform(single value)
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
Support Vector Machines
Cost function for SVM is the cost of misclassification (Lost class).
SVM is Linear model
SVM or Support Vector Machine is a linear model for
classification and regression problems. It can solve linear and
non-linear problems and work well for many practical problems.
The idea of SVM is simple: The algorithm creates a line or a
hyperplane which separates the data into classes.
transfroms non-linear data into linearly-separable data.
Thus we can classify data by adding an extra dimension to it so
that it becomes linearly separable and then projecting the
decision boundary back to original dimensions using mathematical
transformation. But finding the correct transformation for any
given dataset isn’t that easy. Thankfully, we can use kernels in
sklearn’s SVM implementation to do this job.
Regularixation
Outlier Sensitivity
Out of two outliers disturbs the model. For example, a point
close to the other group that is not belonging to makes SVM to
draw the line close to the other group. So in this case,
misclassification should be admitted
So, we use regularization below.
Smaller C, the more regularized.
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC, SVC(?) # LinearSVM for regression.
LinSVC = LinearSVC(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=True, fit_intercept=True,
penalty='l2', random_state=None)
LinSVC = LinSVC.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = LinSVC.predict(X_test)
Kernels
Kernels map hyperplane to the higher dimensional space. Utilizes
similarity metrics (e.g. Gaussian Kernel, Radial Basis Function)
to find out which point is closest to the new point. I.E. apply
Kernel for all data points.
Higher
C and
gamma
means less regulazation and more complex models
from sklearn.svm import SVC
svc = SVC(kernel='rbf', C=1.0, gamma=0.1)
svc = svc.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = svc.predict(X_test)
Faster Kernel Transformation
Nystroem.
n_components
is the number of samples and use cross-validation for
hyperparameters
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import Nystroem
Nystroem = Nystroem(kernel='rbf', gamma=1.0, n_components=100)
X_kernel = Nystroem.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = Nystroem.transform(X_test)
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import RBFSampler
RBFSampler = RBFSampler(gamma=1, n_components=100)
X_kernel = RBFSampler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = RBFSampler.transform(X_test)
Machine Learning Workflow
| Features | Data | Model Choice |
|---|---|---|
| many(~10K) | Small(~1K rows) | Simplle, Logistic, LinearSVC |
| few(<100) | Medium(<10K rows) | SVC with RBF |
| few(<100) | Large(>100K rows) | ADd features, Logistic, LinarSVC or Kernel Approx |

Leave a comment